Trauma Traumatic events such as the loss of a loved one involvement in a violent act or major accident and much more are often the biggest reasons why people get addicted to drugs. Shallow or labored breathing slowing down or cessation of breathing.

The Biology Of Addiction Youtube
Sometimes people with addiction.

. It is known that addiction changes the circuitry of the brain in ways that make it increasingly difficult for people to regulate the allure of an intense chemical rush of reward. However the compulsion to use opioids builds over time to extend beyond a simple drive for pleasure. Doctors define drug addiction as an irresistible craving for a drug out-of-control and compulsive use of the drug and continued use of the drug despite repeated harmful consequences.
The more drugs or alcohol youve taken the more disruptive it is to the brain Researchers have found that much of addictions power lies in its ability to hijack and even destroy key brain regions that are meant to help us survive. Developmental factors in addiction are based on the fact that drug abuse can have an even more detrimental effect on the developing brain than on the adult brain. The brain remembers this feeling and sends out an intense motivation to seek and use the drug again.
As described by the. Drugs have an effect on the way the brain communicates and they can affect the way nerve cells send receive and interpret information. Self-Medicating is one of the top reasons that people abuse drugs and alcohol.
By overstimulating the reward circuit. Gradually it becomes more. Addictions Effect on the Brains Reward System.
Opioids are highly addictive in large part because they activate powerful reward centers in your brain. This is extremely common as individuals who go through traumatic events such as these are in need of quick physical and emotional release. These brain changes can be persistent which is why drug addiction is considered a relapsing diseasepeople in recovery from drug use.
Particularly in the early stages of abuse the opioids stimulation of the brains reward system is a primary reason that some people take drugs repeatedly. When addicted a person continues to use the drug despite the harm caused due to it. 32 It also may result from a mix of early social and biological risk factors including lack of a stable home or family exposure to.
Although taking drugs at any age can lead to addiction research shows that the earlier people begin to use drugs the more likely they are to develop serious problems. The initial decision to take drugs is voluntary for most people but repeated drug use can lead to brain changes that challenge an addicted persons self-control and interfere with their ability to resist intense urges to take drugs. While PTSD isnt limited to individuals with a history of military service anywhere from 35-75 of veterans with the condition are known to abuse drugs and alcohol as a way to cope with.
The addicting drug causes physical changes to some nerve cells neurons in your brain. Self-medication can stem from stress anxiety undiagnosed mental illness severe depression loneliness and trauma. As described in our first post of this blog series alcohol and drug abuse trigger a rush of dopamine in the reward system of the brain.
Addiction Changes Brain Structures and Their Functioning Impaired Decision-making Impulsivity and Compulsivity. Many people visit methadone clinics and get relief from the drug but end up becoming nearly as addicted to methadone as they did the original opioid that caused them problems. Drugs have the potential to significantly impact the systems in the brain relating to pleasure and motivation and make it difficult for other natural pleasures to compare.
Neurons use chemicals called neurotransmitters to communicate. Drug addiction is a disorder in which the brain and the behavior of a person is affected which leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or an illegal drug or medication. This makes us crave more drugs.
People get addicted to drugs for many reasons but one of the major factors behind why drugs are so addictive is the rewarding euphoric high they bring about. These changes can remain long after you stop using the drug. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services.
This increased compulsion is related to tolerance and dependence. This causes the euphoric high that keeps drug users coming back for more. There are cases of people taking methadone for years because they cannot bring themselves to face the withdrawal.
According to the US. All drugs of abuse trigger a surge of dopamine a rush of wanting in the brain. The brain releases a controlled amount of dopamine when you experience natural pleasures.
In the drug-addicted brain the hypothalamus is affected due to abnormal levels of brain chemicals. When most people hear the word addiction they think of dependence on a substance such as drugs or alcoholAnd for good reason. For this reason even experimenting with drugs or alcohol at a young age can make it more likely that youth with develop a problem with addiction later on.
Drugabusegov states that there are two ways this disruption of the brain can happen. How quickly each drug can get into the brain and how powerfully it activates neural circuits determines how addictive it will be Morikawa told Live Science. Drug addiction can start with experimental use of a drug or alcohol.
Your brains basil ganglia and one of its regions the nucleus accumbens basically binge on the. Addiction is a complex chronic disease that affects the brain and occurs due to many different underlying causes. When people begin using drugs the way the brain functions begins to change.
Drugs cause an unnatural dopamine surge. Drugs take control of this system releasing large amounts of dopaminefirst in response to the drug but later mainly in response to other cues associated with the druglike being with people you used drugs with or being in places where you used drugs. If you have Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder or PTSD as well as an addiction to drugs or alcohol this is known as dual diagnosis or a co-occurring disorder.
31 This may be due to the harmful effect that drugs can have on the developing brain. But theres more to what drugs do to the addicted brain than a simple dopamine surge. 1 Scientific research around the world continues to identify various risk factors such as genetics and environment which contribute to.
These reasons and sometimes more than one of these reasons can easily lead a person to begin using drugs and alcohol to cope. Addictions Effect on the Cerebral Cortex Drug Seeking and Cravings. Since the hypothalamus controls the bodys autonomic nervous system many of the functions of the vital organs will be affected such as.
Physical addiction appears to occur when repeated use of a drug changes the way your brain feels pleasure. The brain actually changes with addiction and it takes a good deal of work to get it back to its normal state.
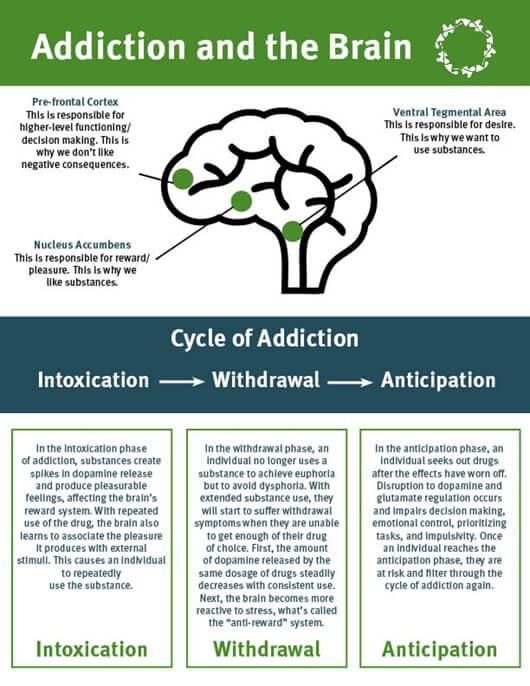
How Does Addiction Affect The Brain Ashley Treatment

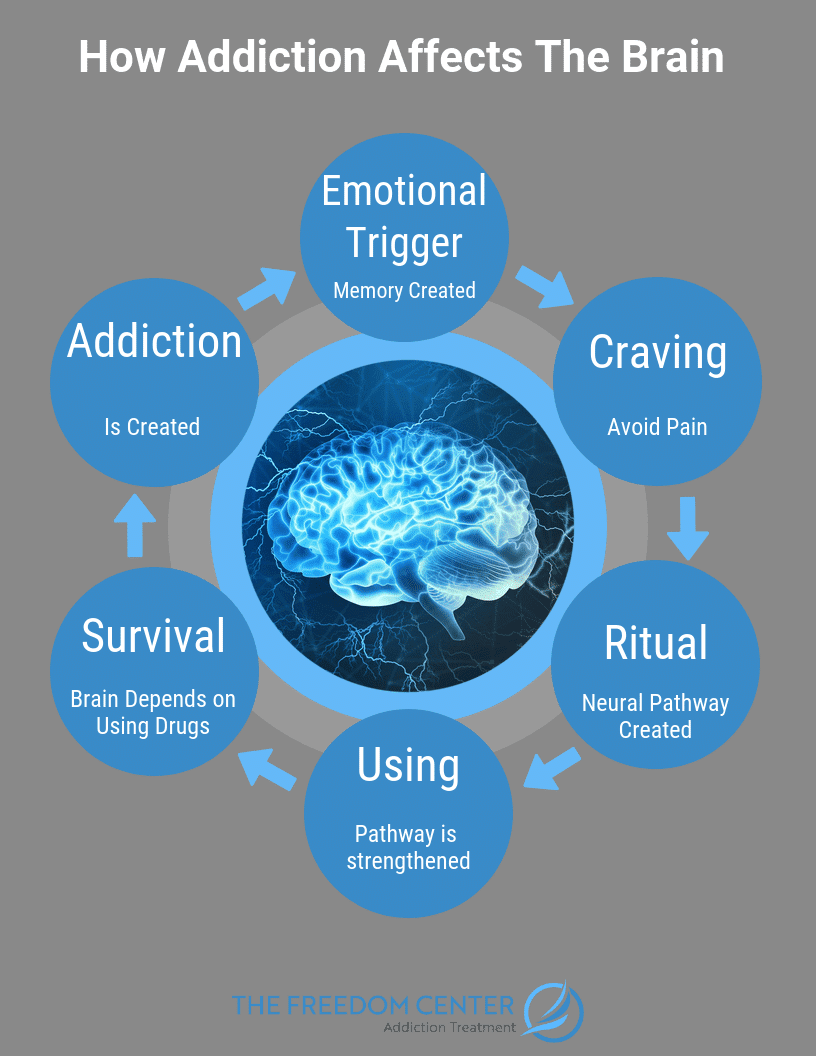
0 Comments